meal planning for beginners pdf
Meal planning is organizing meals in advance, saving time and money while reducing waste. It helps create balanced meals, stick to budgets, and simplify grocery shopping. Essential for beginners.
What is Meal Planning?
Meal planning is the process of organizing and scheduling meals in advance to create a structured approach to eating. It involves deciding on breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks for specific days, ensuring balanced nutrition and variety. This method helps reduce food waste, save time, and stick to budgets by avoiding impulse purchases. Meal planning can be tailored to individual preferences, dietary needs, or lifestyle requirements, such as busy schedules or special diets. It also involves creating shopping lists and preparing ingredients in advance, making it easier to cook wholesome meals. Whether for one person or a family, meal planning is a practical tool for maintaining healthy eating habits.
Why Meal Planning is Important
Meal planning is essential for saving money by reducing food waste and avoiding impulse purchases. It helps manage time by streamlining grocery shopping and daily meal decisions. Planning ensures balanced nutrition, promoting healthier eating habits and better energy levels. It also supports weight management by controlling portion sizes and calorie intake. Additionally, meal planning accommodates dietary restrictions and preferences, making it adaptable to various lifestyles. By organizing meals in advance, it reduces stress and saves effort, making it a practical approach to enhancing overall well-being and maintaining a consistent, nutritious diet.
Benefits of Meal Planning for Beginners
Meal planning offers numerous benefits for beginners, helping them establish a structured approach to nutrition and cooking. It saves time by organizing meals in advance, reducing decision fatigue. Planning encourages healthier eating by prioritizing balanced meals and reducing reliance on fast food. It also fosters financial savings by minimizing food waste and overbuying. Beginners can explore new recipes and ingredients, expanding their culinary skills. Meal planning promotes consistency, making it easier to stick to dietary goals. Additionally, it reduces stress by eliminating last-minute meal decisions. Overall, it’s a practical tool for building healthy habits and improving overall well-being in a manageable way.

Understanding Your Dietary Needs
Identifying your dietary requirements ensures meals align with health goals, preferences, and lifestyle. This step helps beginners create personalized plans that cater to their unique nutritional needs effectively.
Assessing Your Lifestyle and Preferences
Understanding your lifestyle and preferences is crucial for effective meal planning. Consider your daily schedule, cooking skills, and the number of meals you prepare. Think about your food preferences, budget, and how much time you can dedicate to cooking. Ask yourself: Are you often busy, requiring quick meals? Do you enjoy experimenting with new recipes or prefer simple dishes? Assessing these factors helps tailor meal plans to fit your life, ensuring they are practical and enjoyable. This step ensures your meals align with your tastes, schedule, and goals, making meal planning sustainable and stress-free in the long run.
Setting Realistic Goals for Meal Planning
Setting realistic goals is essential for successful meal planning, especially for beginners. Start by identifying achievable objectives, such as cooking at home most weeknights or preparing a few meals in advance. Avoid overly ambitious targets that may lead to frustration. Consider your schedule, budget, and cooking skills when setting these goals. For example, aim to plan three meals a week if time is limited. Break larger goals into smaller, manageable steps to build confidence and consistency. Celebrate progress, no matter how small, to stay motivated. Flexibility is key, as life often requires adjustments. Start small and gradually expand your goals as you become more comfortable with meal planning.
Considering Dietary Restrictions and Preferences
When creating a meal plan, it’s crucial to consider dietary restrictions and preferences to ensure meals are safe, enjoyable, and aligned with personal values. Identify any allergies, intolerances, or preferences, such as vegetarian, gluten-free, dairy-free, or keto diets. Incorporate ingredients that cater to these needs while maintaining nutritional balance. For example, swap gluten-containing grains for alternatives like quinoa or rice; Research recipes that naturally fit these requirements or adapt traditional dishes to suit specific diets. Reading food labels and consulting with a healthcare provider or dietitian can also help tailor meals effectively. This step ensures everyone’s needs are met and fosters a positive eating experience.

Planning Your Meals
Meal planning involves organizing meals in advance to save time, reduce waste, and ensure healthy eating. It helps create balanced meals, prevents decision fatigue, and promotes consistency.
How to Create a Weekly Meal Plan
Creating a weekly meal plan involves assessing your dietary needs, choosing recipes, and scheduling meals. Start by listing breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks for each day. Consider leftovers to minimize waste and save time. Select recipes that align with your skill level and preferences. Plan around ingredients you already have or that are on sale. Assign meals to specific days based on your schedule and energy levels. Make a grocery list of required ingredients. Finally, review and adjust the plan to ensure variety and nutritional balance. This structured approach helps streamline cooking and reduces last-minute decisions.
- Assess dietary needs and preferences.
- Select recipes suitable for your skill level.
- Schedule meals for each day of the week.
- Include snacks and consider leftovers.
- Adjust based on your schedule and preferences.
Using a Meal Planning Template
A meal planning template simplifies the process by providing a structured format for organizing your meals. These templates are readily available online or in PDF guides and often include sections for days of the week, meal types (breakfast, lunch, dinner), and grocery lists. Start by selecting a template that suits your needs, then fill in each day’s meals; Digital templates can be edited and saved, while printable versions allow for handwritten plans. Using a template saves time, reduces decision fatigue, and ensures your meals are balanced and organized. Customize it to include dietary preferences, portion sizes, or nutritional goals.
- Select a template that matches your preferences.
- Fill in meals for each day of the week.
- Include a grocery list for easy shopping.
- Customize for dietary needs and goals.
Choosing Recipes for Beginners
Selecting simple and delicious recipes is key to successful meal planning. For beginners, it’s best to start with recipes that require minimal ingredients and straightforward instructions. Look for one-pot meals, salads, and stir-fries, as they are easy to prepare and versatile. Opt for recipes with familiar flavors to ensure meals are enjoyable. Consider cooking time and choose dishes that fit your schedule, such as quick 30-minute meals for busy days. Use online resources or cookbooks designed for beginners to find inspiration. Ensure recipes align with your dietary preferences and ingredient availability. Avoid overly complex dishes until you gain confidence in the kitchen.
- Choose recipes with minimal ingredients.
- Opt for simple, one-pot, or stir-fry dishes.
- Select recipes with short cooking times.
- Use beginner-friendly cookbooks or websites.

Budgeting and Shopping
Budgeting and shopping are essential for successful meal planning. Plan groceries based on sales, buy in bulk, and avoid waste to save money. Shop smart, eat well.
- Set a grocery budget to manage expenses.
- Shop during sales to reduce costs.
- Bulk buy non-perishable items for convenience.
- Plan meals around affordable ingredients.
How to Budget for Groceries
Creating a grocery budget is crucial for meal planning. Start by determining how much you can afford to spend weekly or monthly. Track your expenses to identify spending patterns and adjust accordingly. Plan meals around seasonal produce and items on sale to reduce costs. Prioritize essential items and avoid impulse buys. Consider budget-friendly protein sources like beans or eggs. Allocate funds for snacks and treats to maintain flexibility. Use cash for shopping to stick to your budget. Finally, review and adjust your budget regularly to reflect changes in prices or preferences; This approach ensures sustainable and stress-free grocery shopping.
Shopping for Ingredients on Sale
Shopping for ingredients on sale is a smart way to reduce grocery costs. Check weekly ads for discounts and plan meals around sale items. Stock up on non-perishables like canned goods, grains, and spices when they’re discounted. Buy seasonal produce, as it’s often cheaper and fresher. Consider purchasing in bulk for items with long shelf lives, like nuts or frozen meats. Use coupons or cashback apps for extra savings. Compare prices between brands and opt for store generics when possible. Avoid buying too many perishables that may go to waste. Stick to your list to stay focused and save money.
Bulk Buying and Avoiding Waste
Bulk buying can save money and reduce waste if done thoughtfully. Focus on non-perishable items like grains, beans, and canned goods, which have long shelf lives. Purchasing meats, cheeses, and bread in bulk can also be cost-effective if properly stored. Freeze items like berries, vegetables, or cooked meals to preserve freshness. Plan meals around bulk ingredients to avoid waste. Use airtight containers and label everything for easy tracking. Avoid buying too much of perishables that may spoil before use. Bulk buying works best when paired with meal prep and a well-organized storage system. This ensures savings and reduces food waste effectively.

Meal Prep and Batch Cooking
Meal prep involves preparing meals in advance, while batch cooking focuses on making large quantities of a single ingredient. Both save time and ensure consistency.
What is Meal Prep?
Meal prep, or meal preparation, is the process of planning, shopping, and preparing meals in advance. It helps save time, ensures healthy eating, and reduces food waste. By organizing meals for the week, individuals can avoid last-minute takeouts and maintain dietary goals. Meal prep often involves portioning ingredients, cooking meals in bulk, and storing them for later consumption. It’s a flexible approach that caters to various lifestyles, preferences, and budgets. Beginners can start by prepping simple meals or components like grains, proteins, and vegetables. Consistency is key to making meal prep a sustainable habit for better nutrition and time management.
Batch Cooking for Beginners
Batch cooking involves preparing large quantities of a single ingredient or dish to use across multiple meals. It’s a time-saving strategy that simplifies meal planning and reduces kitchen time. Beginners can start by cooking staples like grains, proteins, or vegetables in bulk. For example, cooking a large batch of rice or lentils can provide a base for several meals throughout the week; This method also helps reduce food waste and saves money. Start with simple recipes and gradually expand your batch cooking repertoire. Focus on ingredients that freeze well, such as soups or casseroles, to build a convenient freezer stash for future meals.
Freezer-Friendly Meals
Freezer-friendly meals are a game-changer for meal planning, offering convenience and reducing food waste. Many dishes, such as casseroles, soups, and stir-fries, can be prepared in advance and frozen for later use. When freezing, portion meals into individual servings for easy thawing and reheating. Label containers with the dish name and date to ensure nothing goes to waste. Meals like lasagna, chili, and veggie-packed rice bowls freeze exceptionally well. When storing, use airtight containers or freezer bags to prevent freezer burn. Thaw overnight in the fridge or reheat directly from the freezer for a quick, stress-free meal solution.

Tools and Resources
Utilize meal planning apps, websites, and digital tools to organize recipes and groceries. Physical planners, calendars, and whiteboards also help track and manage meal schedules effectively.
Meal Planning Apps for Beginners
Discover how meal planning apps can simplify your journey. Popular options like Plan to Eat, Yummly, and Mealime offer user-friendly interfaces for organizing recipes, generating grocery lists, and tracking meals. These apps often include features such as recipe filtering by dietary preferences, meal scheduling, and nutritional information. For beginners, apps like AnyList and Paprika Recipe Manager are excellent for creating and managing meal plans. They also allow syncing across devices, making it easy to access your plans on the go. Many apps provide step-by-step guides and tutorials tailored for those new to meal planning, helping you stay organized and consistent with your goals.
Creating a Meal Planning Binder
A meal planning binder is a practical tool to organize your recipes, grocery lists, and schedules. Start by dividing the binder into sections like weekly meal plans, recipe ideas, and shopping lists. Include tabs for different categories, such as breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Add clear plastic pockets for storing loose recipes or notes. Customize the binder with a budget tracker and a pantry inventory to keep track of your supplies. Use colorful dividers or stickers to make it visually appealing. Don’t forget to leave space for notes and inspiration. This binder will become your go-to resource for staying organized and consistent with your meal planning goals.
Free Printable Meal Planning Templates
Free printable meal planning templates are a fantastic resource for beginners, offering a structured way to organize meals and groceries. These templates are easily downloadable and customizable to suit individual needs. Many include sections for daily meal schedules, grocery lists, and space for notes. They often feature a clean design, making it simple to plan breakfast, lunch, dinner, and snacks. Beginners can find these templates on various websites or in meal planning PDF guides. Printing them allows for a hands-on approach to planning without relying on digital tools. Using these templates can help streamline the process and keep you consistent with your goals.

Healthy Eating Guides
Healthy eating guides provide foundational knowledge for balanced nutrition, helping beginners make informed food choices and create nutritious meals aligned with their dietary goals and preferences.
Understanding Macronutrients
Macronutrients—carbohydrates, proteins, and fats—are essential for energy and bodily functions. Carbohydrates fuel the brain and body, while proteins build and repair tissues. Fats support brain health and hormone production. Balancing these nutrients ensures sustained energy, weight management, and overall health. For meal planning, understanding macronutrient ratios helps tailor meals to individual needs, such as high-protein diets for muscle growth or low-carb plans for weight loss. Tracking macronutrient intake can enhance meal prep efficiency and promote healthier eating habits. A balanced approach ensures nutritional adequacy and supports long-term wellness goals for beginners.
Portion Control for Beginners
Portion control is a vital skill for managing calorie intake and maintaining a balanced diet. It helps prevent overeating and ensures meals are nutritionally appropriate. A standard serving size is a guide, but portions can vary based on individual needs. Using smaller plates, measuring tools, or pre-portioned containers can help gauge accurate amounts. Pay attention to food labels and adjust servings accordingly. Mindful eating, such as eating slowly and avoiding distractions, also supports better portion management. By mastering portion control, beginners can enjoy their favorite foods while maintaining healthy eating habits and achieving their dietary goals more effectively.
Staying Hydrated
Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and digestion, especially when following a meal plan. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water daily, adjusting for activity levels and climate. Incorporate water-rich foods like fruits and vegetables to boost hydration. Avoid sugary drinks and caffeine, which can dehydrate the body. Carry a reusable water bottle to remind yourself to drink throughout the day. Add slices of lemon or lime for flavor without added calories. Herbal teas and low-sugar juices can also contribute to hydration. Monitor your urine color—it should be pale yellow to ensure you’re drinking enough water. Prioritize hydration to support energy levels and bodily functions.

Special Diets
Special diets cater to unique dietary needs, ensuring balanced and nutritious meals. Meal planning for vegan, gluten-free, or anti-inflammatory diets helps create tailored, delicious, and healthy options for beginners.
Vegan Meal Planning for Beginners
Vegan meal planning focuses on plant-based foods, excluding animal products. Start by incorporating protein sources like beans, lentils, and tofu. Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to ensure nutrient diversity; Plan meals around seasonal produce for freshness and affordability. Use meal planning templates to organize breakfast, lunch, and dinner options. Don’t forget to add healthy fats like avocado, nuts, and seeds. Consider vegan-friendly snacks to avoid hunger between meals. For beginners, simple recipes like stir-fries, salads, and smoothies are great starting points. Meal prepping can save time and help stick to your vegan diet consistently.
Gluten-Free Meal Planning
Gluten-free meal planning involves avoiding foods containing gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. Start by identifying gluten-free grains like rice, quinoa, and corn. Incorporate alternatives such as almond flour and coconut flour for baking. Focus on whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and legumes. Always check labels for gluten-free certification. Plan meals around naturally gluten-free options to simplify the process. Use a weekly planner to organize breakfast, lunch, and dinner ideas. Consider batch cooking gluten-free staples like rice or quinoa. Avoid cross-contamination with gluten-containing foods during preparation. Meal planning apps can help find gluten-free recipes and track ingredients effectively.
Anti-Inflammatory Meal Planning
Anti-inflammatory meal planning focuses on foods that reduce inflammation, promoting overall health. Prioritize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats like avocado and olive oil. Include anti-inflammatory spices such as turmeric and ginger. Avoid processed foods, refined sugars, and fried items that trigger inflammation. Stay hydrated with herbal teas and water. Incorporate fatty fish like salmon for omega-3 benefits. Use meal prepping to ensure consistent, balanced meals. Consider a rotation of anti-inflammatory recipes to keep meals varied and flavorful. This approach supports chronic disease prevention and enhances well-being, making it a valuable addition to any meal planning routine.

Practical Tips
Start small, plan flexibly, and keep meals simple. Use leftovers creatively and prep in advance to save time. Stay organized and adjust as needed for success.
Starting Small
Beginners should start by planning a few meals instead of an entire week. Focus on simple, quick recipes to build confidence. Start with one or two meals a day, like breakfast or lunch, and gradually expand. Keep ingredients minimal and choose one-pot dishes or salads for ease. Plan meals around what you already have to reduce waste. Use weekends to prep basic ingredients like chopped veggies or cooked grains. Celebrate small victories, like cooking at home three times a week. Remember, meal planning is a skill that improves over time. Start slow, stay flexible, and enjoy the process of learning and growing.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
Beginners often make mistakes like overplanning or being too ambitious. Start with realistic goals and simple recipes. Don’t forget to consider your schedule and preferences when planning meals. A common error is buying too much, leading to wasted groceries. Avoid this by checking what you already have. Overcomplicating recipes can discourage you, so stick to basics. Don’t skip meal prep steps, as they save time later. Another mistake is not having a backup plan for unexpected changes. Lastly, avoid being too rigid—flexibility is key. Learn from mistakes and adjust your approach. Meal planning becomes easier with practice and patience.
Staying Consistent
Consistency is key to successful meal planning. Start by establishing a routine, whether it’s planning meals weekly or bi-weekly. Track your progress to stay motivated and identify patterns. Celebrate small victories, like completing a week without takeout. Flexibility is crucial—life changes, so adapt your plan as needed. Set reminders to review and update your plan regularly. Consistency builds habits, making meal planning second nature over time. Don’t be too hard on yourself if you miss a day; simply get back on track. The goal is to create a sustainable routine that fits your lifestyle and keeps you committed long-term.
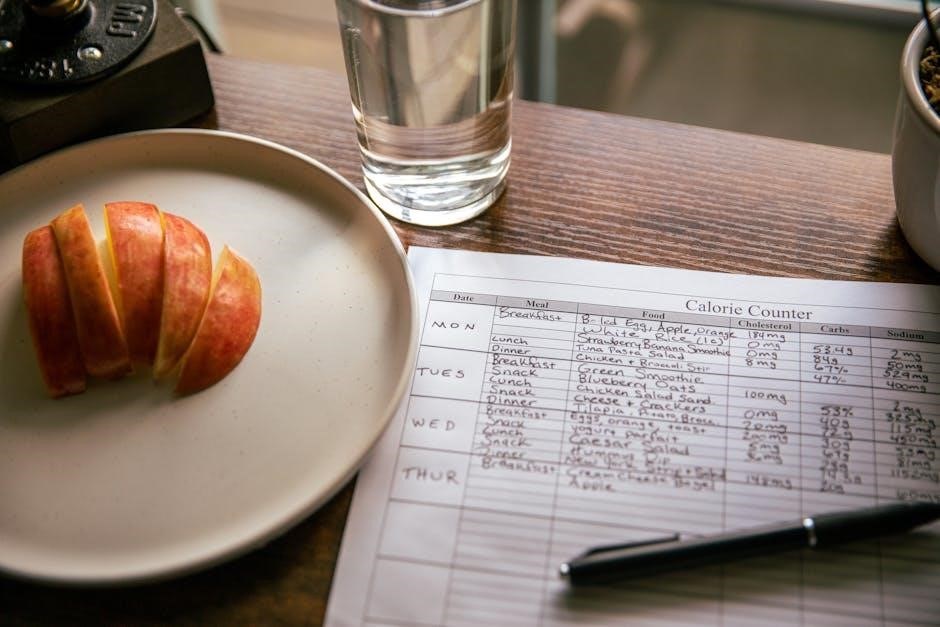
Sample Meal Plans
Sample meal plans provide structured guides for organizing meals. They offer 1-week, 5-day, or 30-day schedules, ensuring variety, nutrition, and simplicity for beginners.
1-Week Meal Plan for Beginners
A 1-week meal plan is a great starting point for beginners. It includes breakfast, lunch, snacks, and dinner options for each day, ensuring variety and balance. Start with simple recipes like overnight oats for breakfast, grilled chicken salads for lunch, and one-pot meals for dinner. Incorporate leftovers to reduce waste and save time. Snacks can include fruits, nuts, or yogurt. This plan helps develop a routine and makes grocery shopping easier. Focus on whole foods, seasonal ingredients, and flavors you enjoy. Adjust portion sizes based on your needs and preferences for a personalized approach to healthy eating.
5-Day Meal Plan
A 5-day meal plan is perfect for beginners, offering flexibility and simplicity. Start with Monday: scrambled eggs for breakfast, a turkey and avocado wrap for lunch, baby carrots as a snack, and baked salmon with steamed vegetables for dinner. Tuesday features Greek yogurt with berries, a grilled chicken salad, an apple with peanut butter, and spaghetti with turkey meatballs. Wednesday includes oatmeal, a tuna sandwich, mixed nuts, and roasted chicken thighs with mashed potatoes. Thursday offers a smoothie, quesadilla, cottage cheese, and stir-fried tofu with rice; Friday ends with pancakes, a chicken Caesar salad, dark chocolate, and beef stir-fry with broccoli. This plan balances variety and ease, helping beginners stay consistent without feeling overwhelmed.
30-Day Meal Plan
A 30-day meal plan is ideal for establishing a consistent routine, helping beginners develop healthy eating habits. Divide the plan into four weekly blocks, each focusing on different meal themes. Week 1: Classic meals like oatmeal, grilled chicken, and fish. Week 2: Introduce variety with stir-fries, soups, and salads. Week 3: Incorporate quick, one-pot dishes and batch-cooked meals. Week 4: Experiment with new proteins and flavors, like lentils or shrimp. Include a mix of breakfast, lunch, snacks, and dinner options, ensuring balance and nutrition. Batch cooking and prep tips are included to save time. Customize based on preferences and dietary needs for a personalized approach to long-term meal planning success.
Meal planning is a powerful tool for beginners to save time, reduce expenses, and enjoy healthier meals. Stay consistent, and it becomes second nature!
Final Thoughts on Meal Planning
Meal planning is a transformative habit that simplifies life, enhances health, and saves resources. By organizing meals in advance, beginners can avoid last-minute decisions, reduce food waste, and ensure balanced nutrition. It fosters consistency, helping to maintain healthy eating habits and long-term wellness. While it may feel overwhelming at first, the benefits of meal planning far outweigh the initial effort. Embrace it as a flexible tool that adapts to your lifestyle, preferences, and goals. With practice, meal planning becomes second nature, empowering you to take control of your diet and enjoy the journey toward healthier, more organized living.
Next Steps for Beginners
Once you’ve grasped the basics of meal planning, it’s time to take actionable steps. Start by creating a simple weekly plan, focusing on a few meals to build confidence. Use a meal planning template or app to stay organized. Make a grocery list and stick to it to avoid impulse buys. Begin prepping small portions of ingredients to save time during the week. Experiment with new recipes and flavors to keep things exciting. Stay consistent, but remain flexible—life’s unpredictability is okay! Celebrate small victories and gradually expand your planning skills. Remember, the goal is progress, not perfection.
Maintaining a Meal Planning Routine
Maintaining a meal planning routine requires consistency and adaptability. Set a specific day each week to plan meals and shop for groceries. Use digital apps or planners to keep track of recipes and ingredients. Be flexible to accommodate unexpected changes, like last-minute meetings or ingredient shortages. Celebrate small victories, such as completing a week without food waste. Regularly review your meal plan to adjust for new preferences or dietary needs. Over time, meal planning becomes second nature, saving time and reducing stress. Stay committed, and enjoy the long-term benefits of a well-organized kitchen and healthier eating habits.


